Question 1
Type: Array/2D Array
Blog This FRQ was interesting and a good review in many ways because it required me to return back to basics but also requried me to think about new applications. The Key Algorithm was Array iteration and comparison, as it went over different types of arrays and how to get information from them, therefore iterating over them. This key algorithm fits into the type because array iteration and comparison falls into arrays.
Part A
Calculate Array Sum - Iterate through an array and sum its elements

public static int arraySum(int[] arr)
{
int sum = 0;
for(int n : arr)
sum += n;
return sum;
}
// Testing
int[] array = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.print("Original Array: ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
System.out.print("Sum: ");
System.out.print(arraySum(array)); // should return 6
Original Array: [1, 2, 3]
Sum: 6
Part B
Check Array Diversity - Use the array sum to determine if arrays are diverse by comparing their sums.

public static int[] rowSums(int[][] arr2D)
{
int[] sums = new int[arr2D.length];
for(int i = 0; i < sums.length; i++) {
sums[i] = arraySum(arr2D[i]);
}
return sums;
}
// Testing
int[][] my2DArray = { {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}};
System.out.println("Sample get: ");
System.out.print(my2DArray[0][1]); // Output: 2
System.out.println("\nSum");
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(rowSums(my2DArray))); // Output: [6, 15, 24]
Sample get:
2
Sum
[6, 15, 24]
Part C
Diverse Arrays in 2D Array - Check each row of a 2D array for diversity using the methods from parts (a) and (b).
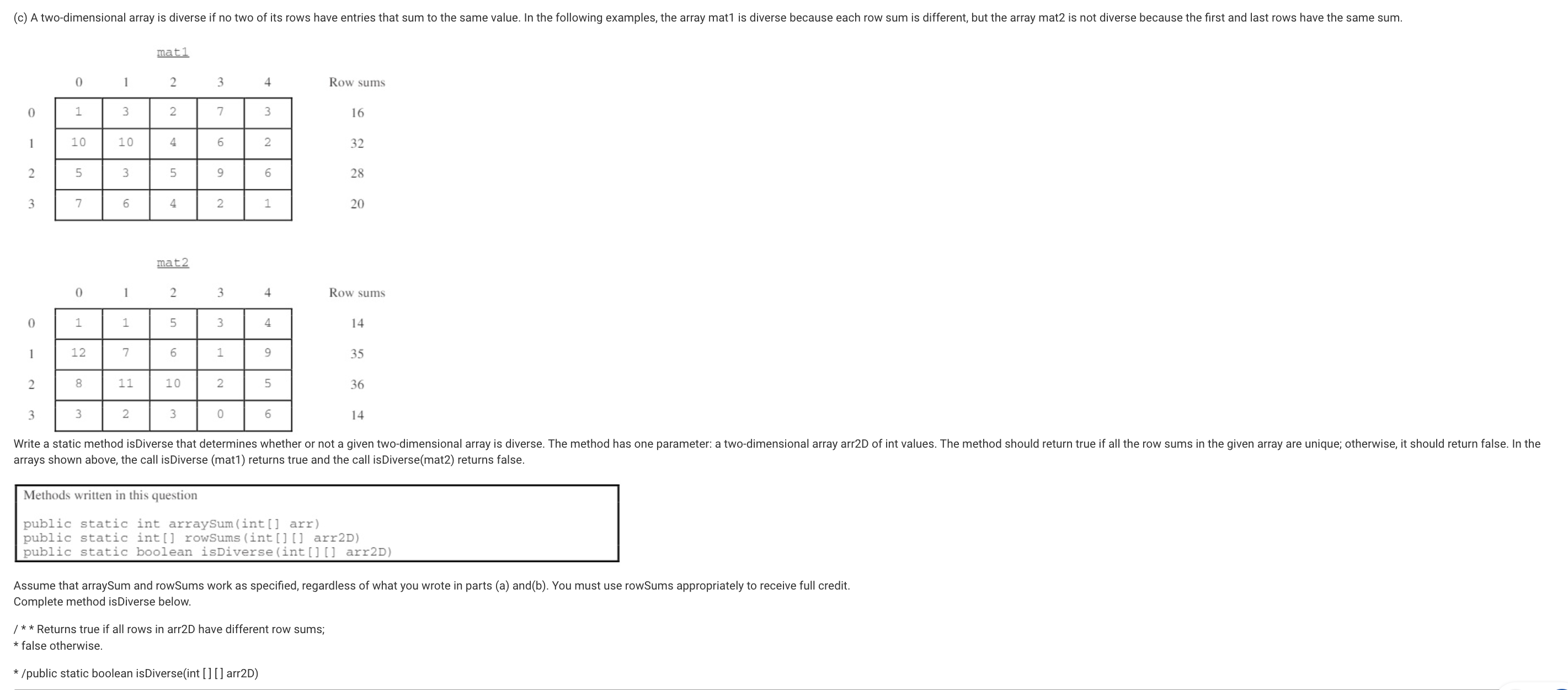
public static boolean isDiverse(int[][] arr2D)
{
int[] sums = rowSums(arr2D);
for(int i = 0; i < sums.length; i++)
for(int j = i+1; j < sums.length; j++)
if(sums[i] == sums[j])
return false;
return true;
}
// Testing
int[][] my2DArray = { {1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}};
System.out.println("First Array Sum");
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(rowSums(my2DArray)));
System.out.println("Is the first array diverse? ");
System.out.println(isDiverse(my2DArray));
System.out.println();
int[][] my2DArray2 = { {3, 2, 1}, {1, 2, 3}, {2, 3, 1}};
System.out.println("Diverse Array Sum");
System.out.print(Arrays.toString(rowSums(my2DArray2)));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Is the second array diverse? ");
System.out.print(isDiverse(my2DArray2));
First Array Sum
[6, 15, 24]Is the first array diverse?
true
Diverse Array Sum
[6, 6, 6]
Is the second array diverse?
false